Introduction
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions. Located in the front of the neck, this small, butterfly-shaped gland produces hormones that control metabolism, growth, and development. However, when the thyroid gland fails to function optimally, it can lead to a condition known as low thyroid function or hypothyroidism. In this article, we will explore the symptoms associated with low thyroid function and shed light on thyroid diseases.
Overview of Thyroid Function and Hormones
Before delving into the symptoms of low thyroid function, it is essential to understand the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones are responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism, temperature, heart rate, and energy levels.
Symptoms of Low Thyroid Function
2.1 Fatigue and Weakness
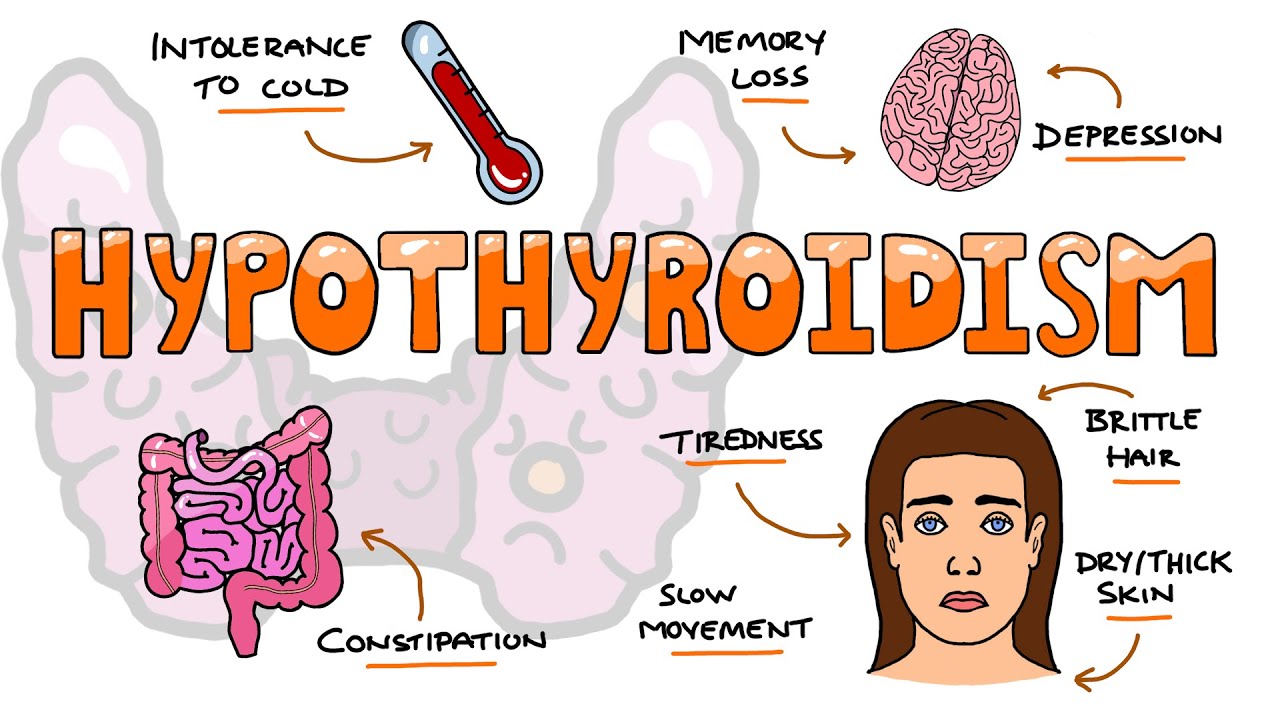
One of the most common symptoms of low thyroid function is persistent fatigue and weakness. Individuals with hypothyroidism often experience a lack of energy, even after getting sufficient sleep. This fatigue can impact their overall productivity and quality of life.
2.2 Weight Gain
Unexplained weight gain is another prevalent symptom of low thyroid function. A slower metabolism caused by hypothyroidism can lead to weight gain despite maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
2.3 Cold Sensitivity
Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating body temperature. Therefore, individuals with low thyroid function may feel more sensitive to cold temperatures. They may find it challenging to stay warm even in mildly chilly environments.
2.4 Dry Skin and Hair
Dry skin and hair are common symptoms of hypothyroidism. The lack of thyroid hormones can affect the skin’s ability to retain moisture, resulting in dryness, itching, and flakiness. Similarly, hair may become dry, brittle, and prone to thinning.
2.5 Muscle and Joint Pain
Hypothyroidism can cause muscle and joint pain, making everyday tasks more challenging. This pain is often described as achy, stiff muscles or joints, which can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
2.6 Constipation
Thyroid hormones play a role in regulating the digestive system. When thyroid function is compromised, the digestive tract may slow down, leading to constipation. Individuals with hypothyroidism may experience infrequent bowel movements and difficulty passing stool.
2.7 Mood Changes
Low thyroid function can affect a person’s mood and mental well-being. Individuals may experience symptoms such as depression, irritability, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating. These mood changes can impact personal relationships and overall emotional health.
2.8 Menstrual Irregularities
Thyroid hormones influence the menstrual cycle in women. When thyroid function is low, menstrual irregularities may occur. Women with hypothyroidism may experience heavier or more prolonged periods, irregular cycles, or even fertility issues.
Thyroid Diseases
3.1 Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
The most common cause of low thyroid function is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. This chronic inflammation gradually impairs thyroid function, leading to hypothyroidism.
3.2 Iodine Deficiency
In areas where iodine intake is insufficient, individuals are at risk of developing iodine deficiency disorders, including goiter and hypothyroidism. Iodine is an essential component required for the production of thyroid hormones.
3.3 Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis refers to the inflammation of the thyroid gland, often caused by a viral infection or an autoimmune condition. This inflammation can lead to
the release of excess thyroid hormones initially, causing a temporary state of hyperthyroidism, followed by low thyroid function or hypothyroidism. Thyroiditis can be a self-limiting condition, resolving on its own over time, or it may require medical intervention.
3.4 Congenital Hypothyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism is a condition that affects infants from birth. It occurs when the thyroid gland fails to develop correctly or doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications in growth and development.
3.5 Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is relatively rare but can occur in individuals with thyroid nodules or a history of radiation exposure. While not directly causing low thyroid function, thyroid cancer treatment, such as surgery or radiation therapy, may result in a decrease in thyroid hormone production, leading to hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you may have low thyroid function, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They will evaluate your symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and order blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels. These tests typically include measuring TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and T4 levels.
Treatment for low thyroid function involves hormone replacement therapy. Synthetic thyroid hormone medications, such as levothyroxine, are prescribed to restore hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. The dosage will be adjusted based on regular monitoring of hormone levels and individual response.
Conclusion
Low thyroid function, or hypothyroidism, is a condition that affects numerous individuals worldwide. Understanding the symptoms associated with this condition is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment. If you experience persistent fatigue, unexplained weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin and hair, muscle and joint pain, constipation, mood changes, or menstrual irregularities, it may be worth consulting a healthcare professional to evaluate your thyroid function.
Thyroid diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, thyroiditis, congenital hypothyroidism, and thyroid cancer, can contribute to low thyroid function. Each condition requires specific management and treatment approaches.
Remember, diagnosing and treating low thyroid function should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. With proper diagnosis, medication, and ongoing monitoring, individuals with low thyroid function can lead healthy and fulfilling lives, managing their symptoms effectively.