Unveiling the Impact of the Recent Sincitial Respiratory Virus Outbreak
Introduction
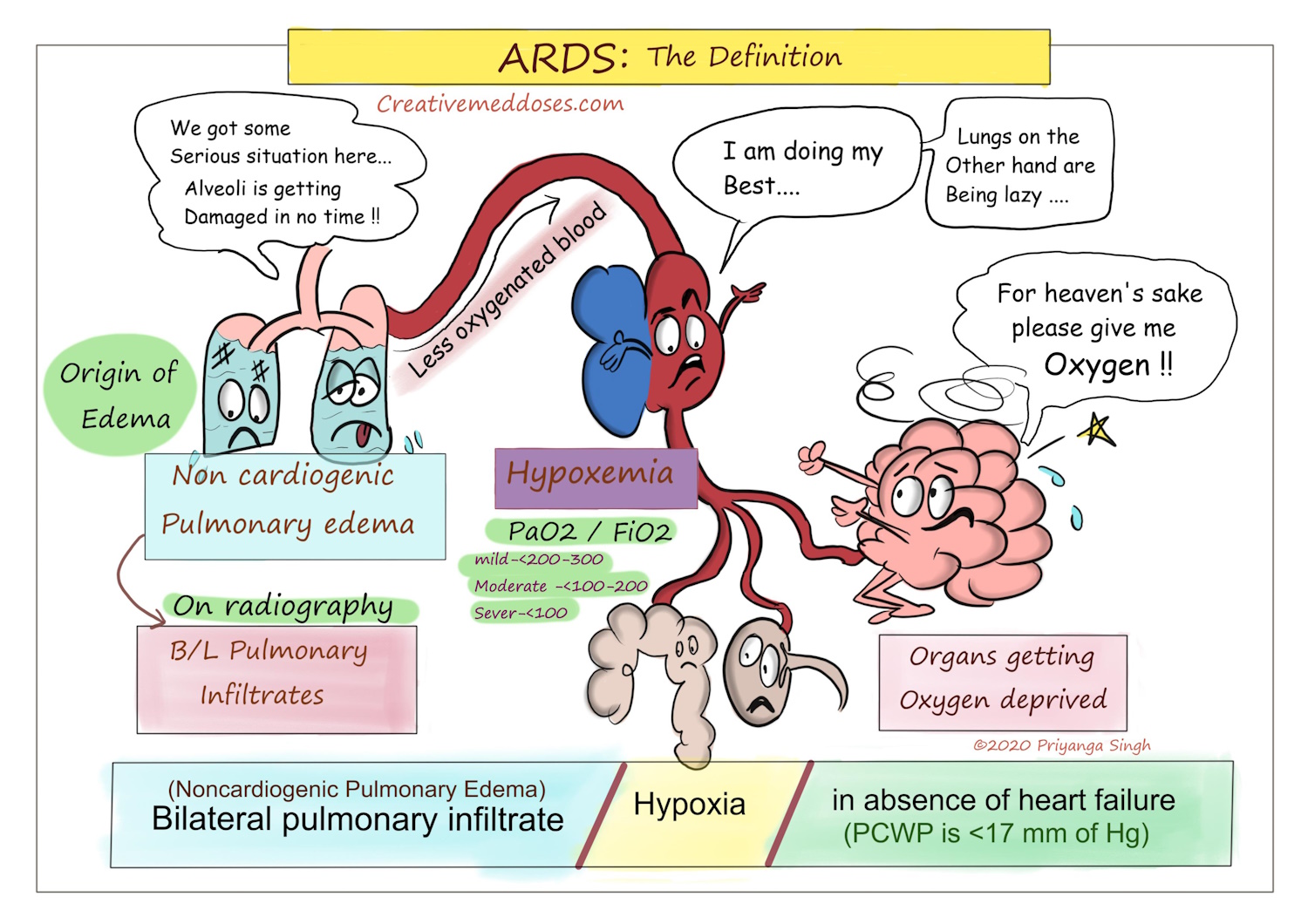
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening condition that affects the respiratory system, characterized by severe and sudden respiratory failure. ARDS is a grave concern for public health, with various factors triggering its onset, including viral infections. One such alarming outbreak is the recent surge in cases of the Sincitial Respiratory Virus (SRV), an infectious agent notorious for its ability to induce severe respiratory distress. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of ARDS, with a specific focus on the latest SRV outbreak, examining its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and potential interventions.
The Pathophysiology of ARDS
ARDS occurs when the lungs’ air sacs, called alveoli, become inflamed and filled with fluid. This inflammation and fluid accumulation result in reduced oxygen levels in the bloodstream, leading to respiratory failure. The condition often arises due to an injury to the lungs, which can be triggered by various factors such as infections, trauma, or inhalation of harmful substances.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Individuals with ARDS typically exhibit a range of symptoms that reflect the compromised respiratory function. These symptoms include rapid and shallow breathing, severe shortness of breath, low blood oxygen levels, and the characteristic crackling sound heard during breathing, known as crepitations. The patients often struggle to maintain adequate oxygenation, leading to increased heart rate and potential multi-organ dysfunction.
Understanding Sincitial Respiratory Virus (SRV)
The Sincitial Respiratory Virus (SRV) is a single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family. It is notorious for its ability to cause severe respiratory infections, particularly in infants, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. SRV is highly contagious and is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets, making it a significant public health concern, especially in crowded settings such as schools and hospitals.
The Recent SRV Outbreak: Unmasking the Threat
In recent times, a notable surge in SRV cases has been observed, raising alarm bells within the medical community and public health organizations worldwide. The outbreak has been associated with a higher incidence of ARDS cases, further emphasizing the virus’s potential to induce severe respiratory distress.
Link between SRV and ARDS: Unraveling the Connection
The connection between SRV and ARDS lies in the virus’s ability to trigger a robust immune response and inflammatory cascade within the respiratory system. As SRV infects the respiratory epithelial cells, the body’s immune system reacts by releasing a surge of pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to the recruitment of immune cells to the site of infection. This inflammatory response can be excessive and uncontrolled, eventually causing damage to the lung tissue and the development of ARDS.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosing ARDS involves a combination of clinical assessment, radiological findings, and laboratory tests. Chest X-rays often reveal bilateral opacities or “white-out” areas in the lungs, indicative of fluid accumulation. Additionally, blood tests may show low blood oxygen levels and abnormal levels of inflammatory markers. Differential diagnosis is essential, as ARDS shares similarities with other respiratory conditions such as heart failure and pneumonia.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing ARDS often involves addressing its underlying causes. In the context of the recent SRV outbreak, stringent infection control measures are crucial to limit the virus’s spread. This includes thorough hand hygiene, proper respiratory etiquette, and isolation of infected individuals. Vaccination efforts also play a pivotal role in reducing SRV transmission and subsequently lowering the risk of ARDS.
Innovations in Treatment Approaches
The management of ARDS typically centers around providing supportive care while addressing the underlying cause. In the case of SRV-induced ARDS, antiviral medications and immune-modulating therapies are under investigation. Recent advances in immunotherapy and targeted antiviral agents hold promise for more effective treatment options, potentially reducing the severity of ARDS and improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome remains a critical challenge in the field of respiratory medicine, with viral infections like SRV contributing to its prevalence. The recent outbreak of Sincitial Respiratory Virus serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust infection control measures, early diagnosis, and effective treatment strategies. As we continue to unravel the complex interplay between viruses and ARDS, ongoing research and innovation hold the key to mitigating the impact of such outbreaks and reducing the burden of this life-threatening condition on global public health.